Galaxy customers often ask our team, “Why do results for a Bartonella ePCR test take 3 weeks?” By the time a customer has decided to get a Bartonella ePCR triple draw test they may have had symptoms for some time, seen many doctors, and made difficult decisions about where to spend their healthcare dollars. We know you want results quickly!
Research shows that the Bartonella bacteria that make people sick can cause a cyclical bacteremia. That means that sometimes the bacteria is in the blood and sometimes it isn’t. This allows the bacteria to evade the host immune response and makes it very hard to test for.
The Bartonella spp. ePCR Triple Blood Draw is an advanced testing method that increases the likelihood of detecting Bartonella species in a sample. The triple draw involves collection of blood and blood serum samples on three different days over a 5 to 7-day period to match the cyclical behavior of Bartonella. In a research study of veterinary staff, the sensitivity of ePCR was about doubled when samples from three different days were tested versus just one.
But this is just the first part of the advanced methods Galaxy Diagnostics uses. How are the samples processed once the lab receives them?
Culturing
Culturing is a common method that clinical diagnostic companies and researchers use to grow microorganisms under controlled laboratory conditions. Clinical samples such as blood are added to a liquid or gel-like growth medium to grow bacteria of interest to a detectable level.
The formulation of the growth medium varies depends on the bacteria being targeted. There are a variety of growth media that are commonly used in clinical laboratories. For example, a lab may use a growth medium called Luria broth to look for multiple bacteria species that do not have specialized growth requirements.
Galaxy Diagnostics uses Bartonella alphaproteobacteria growth medium, or BAPGM, a patented growth medium that selectively grows Bartonella species. It was developed at North Carolina State University by Dr. Ed Breitschwerdt and Dr. Ricardo Maggi, who are respectively the chief scientific officer and chief technology officer of Galaxy Diagnostics.
Since Bartonella species can survive in arthropods such as ticks, the medium formulation was modified to mimic arthropod growth requirements more closely. By matching the environment where the bacteria could normally be found, there is a higher chance of successfully growing the infectious bacteria in the lab. Galaxy Diagnostics scientists have published findings related to the analytical utility of pre-enrichment BAPGM in peer-reviewed journals. A selected list of these publications can be found here.
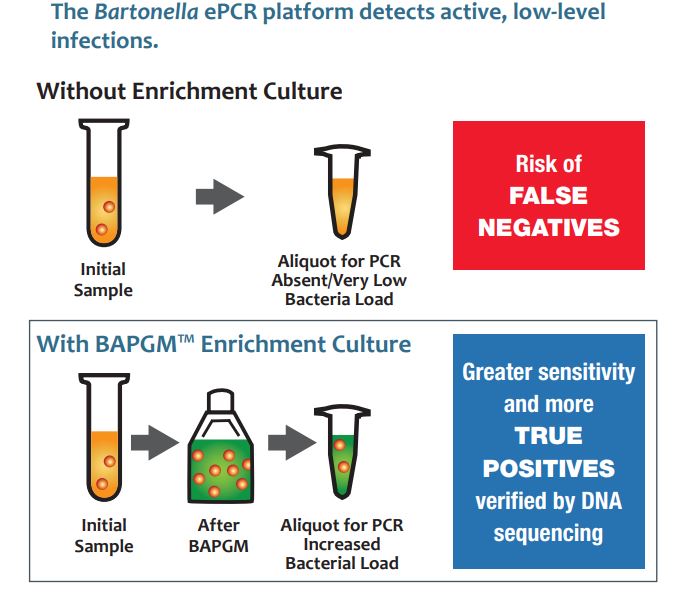
When whole blood samples for Bartonella species testing are received, a BAPGM culture is prepared for each one. The cultures are incubated for a week, during which environmental parameters are strictly monitored and adjusted as needed. Since Bartonella species require 22-24 hours to replicate, it can take a week for substantial growth to occur. By comparison, this is more than 20 times slower than the replication rate of Streptoccocus pygones, the bacteria responsible for strep throat.
Pre- and Post-Enrichment PCR
Polymerase chain reaction, or PCR, is a method of detecting target bacterial DNA in a sample. Performing PCR on a sample after allowing bacteria to grow maximizes the chance of detecting present DNA. This “enrichment” of the sample is where the “e” in ePCR comes from. Research shows that Bartonella species infect at low levels, so using PCR after culturing reduces the chance of false negatives.
The PCR process starts by using a DNA primer (a small fragment of DNA) that a diagnostic or research lab designs to bind to target DNA (“anneal”). An enzyme is then used to amplify the DNA that is present. This process is repeated to maximize the amount of DNA present.
Galaxy combines the previously described culturing step with PCR to maximize the sensitivity and specificity of the test. The broad-spectrum primers can detect a range of pathogenic Bartonella species that may be present in samples. This means that more species can be detected in a single test.
DNA Sequencing
If PCR detects target DNA in a sample, the laboratory still may not know what species of Bartonella was found. There’s even a possibility the primer has annealed to an unexpected microbe. The next step is DNA sequencing to verify that the DNA detected in a sample is what the test is designed to find and to determine the species of bacteria that is present.
Additional Testing
The Bartonella spp. ePCR Triple Blood Draw panel can include a Bartonella IFA serology panel, IgG for B. henselae and B. quintana. This serology panel can also be ordered separately, and a Single Blood Draw ePCR test is available.
Galaxy Diagnostics also offers testing for other vector-borne pathogens and Borrelia burgdorferi ELISA and Western blot. A new serology panel includes Bartonella and Lyme Borrelia serology testing.
The complete Galaxy Diagnostics testing menu can be found here. More about the ordering process can be found here.