Cat scratch disease is a result of acute Bartonella henselae infection.
Bartonella henselae is an emerging pathogen that was first linked to cat scratch disease (CSD) or cat scratch fever  after research on infected HIV patients during the 1990s. The infection is commonly referred to as CSD or cat scratch fever due to symptoms these bacteria can cause following a scratch from a cat. However, a cat scratch is not the only way patients can become ill.
after research on infected HIV patients during the 1990s. The infection is commonly referred to as CSD or cat scratch fever due to symptoms these bacteria can cause following a scratch from a cat. However, a cat scratch is not the only way patients can become ill.
B. henselae is a flea-borne bacterium that is primarily carried and transmitted by fleas (Ctenocephalides felis) found on cats . People that work in animal health occupations, like veterinary staff and shelter workers, are at a higher risk for CSD and other flea-borne illnesses.
There are a variety of symptoms that can occur weeks to months after becoming infected. Common symptoms of CSD include, but are not limited to:
- Low-grade fever
- Swollen or tender lymph nodes
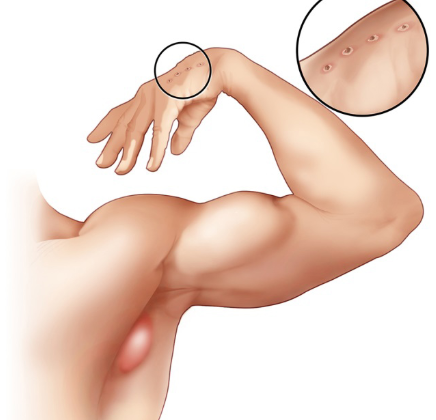
- Fluid filled bump at site of the scratch
- Reddened skin that is warm to the touch
People that are immunocompromised may experience more severe symptoms. If you think you are experiencing symptoms related to CSD, seek medical attention and consider ordering Bartonella Digital ePCR testing to confirm infection.
Learn more about Bartonella species infections with our free medical education webinar and educational webpage From Cat Scratch Disease to Bartonellosis