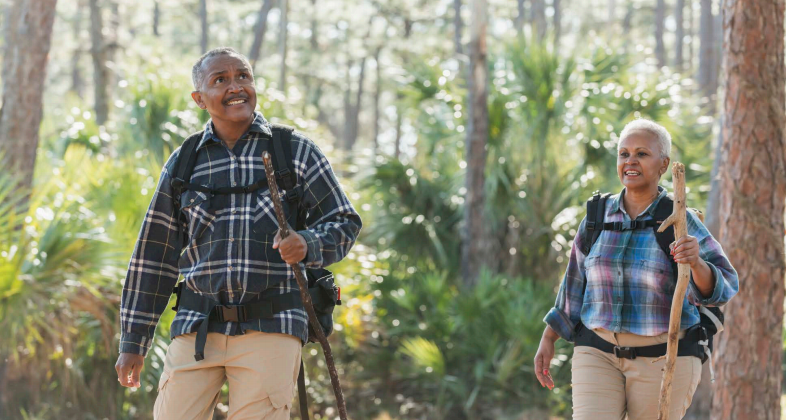
Prevention of tick-borne disease in the United States is at a crossroads of peril and opportunity. On the one hand, researchers have identified innovative and achievable methods for reducing the risk of disease in the environment. On the other hand, emerging diseases and species brought to the United States present new challenges.
The Tick-Borne Disease Working Group (TBDWG) has identified challenges to prevention implementation. These include:
- Personal and/or household protective measures can be expensive.
- Community efforts are difficult to sustain due to shifting regulations and labor demands.
- Citizens may not be aware of the need to take protective measures due to gaps in education and awareness.
- Successful prevention is dependent on integrating public advocacy, scientific progress, and federal engagement.
The TBDWG has made the following recommendations to prevent tick-borne disease:
4.1. Fund additional studies and activities on the development and evaluation of novel and traditional tick-control methods that have shown promise in other areas of public health entomology.
Traditional methods of prevention, such as skin repellents and protective clothing, are critical as a first line of defense against tick-borne disease. Nevertheless, the public has concerns regarding the long-term health and environmental effects of effective pesticides such as Permethrin. The TBDWG recommends more research on the effectiveness of active ingredients in commonly sold natural products, such as soybean or peppermint oil. 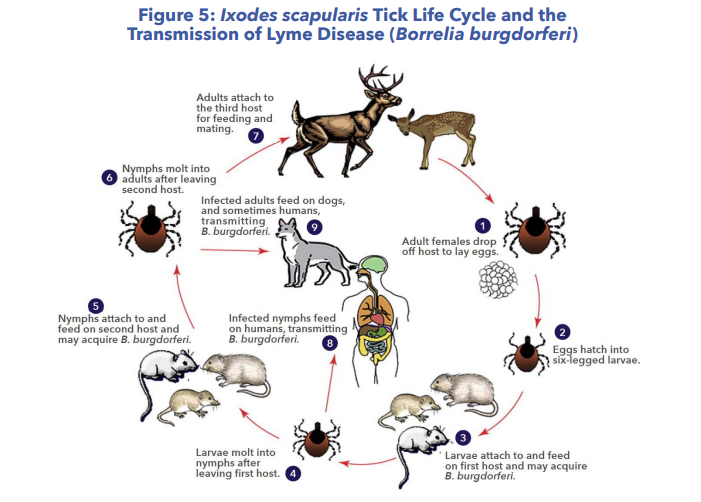
Novel methods, including rodent-targeted vaccinations and genetic approaches, have advocates in the scientific community, but government and public entities remain hesitant. The OspA vaccine for Borrelia burgdorferi (the bacteria that causes Lyme disease) has shown promise in studies, but public concerns about a vaccine remain high. In any case, a vaccine for one pathogen would not reduce tick abundance and the risks from other tick-borne pathogens.
Research on genetically modified organisms is another area of promise, with significant experience in crop management. However, this is also an area where public concern is high. Further research regarding long-term effects on hosts and vectors is necessary before a practical, wide-scale approach is feasible. The TBDWG recommends that funding and activities be focused on researching RNAi technology and transgenic organisms to develop more effective prevention strategies in the future.
4.2 Build trust via a transparent mechanism by which all stakeholders examine and discuss past vaccine activities and potential adverse events to inform future vaccine development in Lyme disease.
And
4.3 Support the development of safe and effective human vaccines to prevent Lyme disease with transparent mechanisms by which all stakeholders examine and discuss past vaccine activities and potential adverse events to inform future vaccine development.
The development of a vaccine against Lyme disease is controversial due to concerns regarding accessibility and health effects. The TBDWG recommends transparency with various stakeholders to further the current development of such a vaccine. It is important to discuss the historical issues that affect the public trust as well as current adverse event concerns to help build trust and stakeholder engagement moving into the future.
The TBDWG recommends improving preventative education because it is necessary in the absence of effective tick control strategies. They have provided multiple suggestions, including posting educational material on public land for visitors and performing social marketing surveys to understand the barriers to accessing information in groups whose current awareness levels are low.
Throughout the chapter, the TBDWG emphasizes that prevention of Lyme disease and co-infection is dependent on various factors, but one of the main keys is education. This is true for both researchers, who must understand these infections and how they are transmitted before they can successfully create tools and methods of prevention, and the general public, who need to make use of whatever prevention tools are available.
Education is a common thread throughout the TBDWG report. Every issue touched on in this series of blog posts about the TBDWG includes the need for more research and more education. At Galaxy Diagnostics, it is our goal to keep patients and physicians informed with the best science-backed information about tick-borne disease. Please subscribe to our blog using the sign-up form to receive e-mail notifications when new posts are published.
The graphics in this post can be found in the TBDWG 2018 Report to Congress.
Want to read more about the report? Click the links below.